Just as technologies and societal/business evolutions are transforming the ways we organize activities such as marketing and customer service, other important business activities are rapidly impacted as well. This is also the case for cybersecurity.
The role of security is evolving and so are the viewpoints, processes, functions, strategies and technological aspects regarding cybersecurity – with a clear evolution towards security in the cloud and an increasing use of artificial intelligence and cognitive computing in today’s pro-active security solutions.
Cybersecurity in transformation
We’ve mentioned before how cybersecurity challenges and gaps in the perceived importance/maturity of security on one hand and the security reality in the field on the other are standing in the way of strategic digital transformation success.
In the end, security is an essential conditio sine qua non of a solid digital business approach.
We’ve also looked at how so-called innovation accelerators such as IoT (Internet of Things) bring a set of new security challenges with them and how changing security perimeters and digital transformation force us to look differently at cybersecurity.
One could say that security as we know it is disrupted. As a matter of fact, many of the non-technological drivers of digital transformation are also key drivers in the transformation of cybersecurity.
Challenges necessitating a different security approach
There are multiple mutual relationships between digital transformation (drivers) and security.
- Compliance and regulatory requirements and changes, on top of the increasing importance of data, directly affect security.
- One of the key traits of today’s digital economy, the high interconnectedness of technologies and processes in a de facto collaborative context, drives demand for heightened security guarantees and SLAs across business ecosystems and value chains.
- In an increasing number of industries digital transformation and disruption mean the creation of partnerships and technological collaborations whereby security is at the very center of the collaborative value propositions which are sought. Think about collaborations in Fintech, for instance, where security simply can’t be an afterthought.
- The move away from legacy systems, which happens at different speeds in various countries and sectors, to cloud environments, fits in the shift from a focus on IT and systems to the business with organizations expecting to be able to innovate and enhance their business operations, while the best possible security is guaranteed.
These drivers are real and, just as cybersecurity needs to play an important role in digital transformation, the causes and consequences of digital transformation are also leading to a disruption and transformation of security itself.
It is all highly inter-connected indeed and there are ample more examples of drivers and evolutions leading to the very transformation of cybersecurity as a mission-critical task and strategy that stretches beyond divisions, branches and the ecosystem in which the connected enterprise resides.
Security drives the urgency to digitally transform
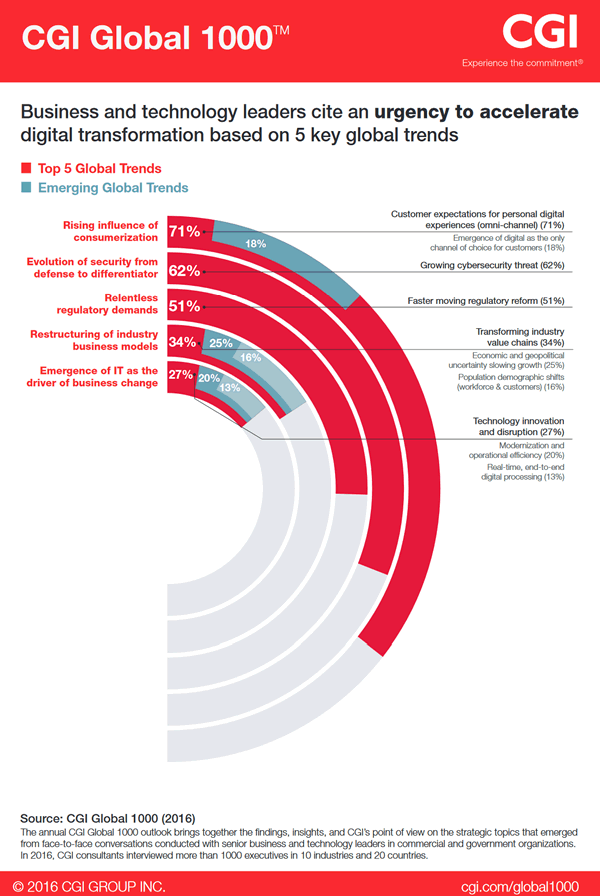
In its 2016 Global 1000 outlook™, CGI identified five key trends which organizations identified as reasons to intensify their self-reported need to transform.
On top of the usual suspects of digital transformation such as the growing impact of consumers’ digital behaviors and phenomena such as the emergence of IT as a driver of business change, CGI found that the evolution of security from defense to differentiator is cited by respondents as a driver of this urgency to accelerate digital transformation. The main reason: the growing cybersecurity threat. Moreover, just as IT overall is seen as a driver of business change, the same business focus is expected from CISOs (Chief Information Security Officers).

Another global trend are “relentless regulatory demands” which we mentioned earlier and are moving faster and faster. Even other identified trends such as the restructuring of business models and transformation of industry value chains have an impact on the need to transform security, as we also mentioned earlier.
On top of the fact of the findings by CGI that for 62 percent of organizations, security is starting to become a differentiator, there is another interesting link between security and digital transformation which we briefly touched upon in our article on the cybersecurity maturity challenges to succeed with digital transformation.
Smart security strategies accelerate digital transformation
According to research by Dell and Dimensional Research (The Digital Transformation Security Global Survey), 96 percent of respondents face challenges securing the several technologies they deploy in the context of their digital transformation efforts.
That’s virtually everyone. Yet, at the same time, security gets in called late. Too late, according to 76 percent of respondents. One of the reasons is very understandable and human but cannot be accepted in this digital economy and leads us to a further need to transform cybersecurity as a practice and its role in the organization: 85 percent of respondents say that business users “avoid engaging with security teams out of concern that their initiatives might be blocked”. Yet, at the same time 63 percent say those concerns are unfounded.
What these findings mean is that, if security issues arise (and are tackled) in virtually all digital transformation projects sooner or later and security is not involved, ill-prepared or stepping in too late, the digital transformation project is slowed down. Or, the other way around, involving security in an integral and timely way in digital transformation initiatives accelerates them!
Add to that the findings of CGI which indicate that compliance – as a driver – and security as such accelerate the need organizations perceive to “transform” and the picture becomes clear.
In conclusion: security is the often overlooked ally of digital transformation
To conclude, a smarter security approach is an enabler and accelerator of digital transformation and of today’s digital and connected business overall, among others driven by increasing regulatory needs.
On top of it all, the place of cybersecurity in the organization, the strategies and as a consequence solutions (pro-active, in the cloud, using analytics and thus artificial intelligence and Big Data) are being “disrupted” as well.
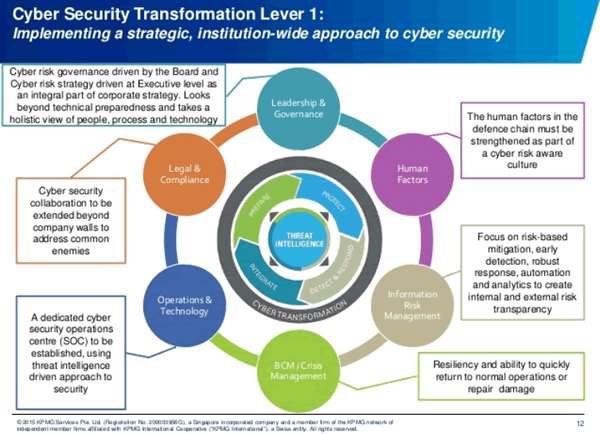
You can imagine that the same goes for the various functions that are typically involved in the overall security picture. But all that is for later contributions.






