The number of patent applications and inventions in the scope of fourth industrial revolution technologies (4IR) is growing and is another token of the rise of industrial transformation – what evolutions and findings regarding patent applications per category of 4IR technologies tell.
Regardless of the question whether the fourth industrial revolution is truly a revolution or rather an evolution: 4IR technologies are showing myriad signs of rapid growth.
This growth is not just seen when looking at investments in Industry 4.0 technologies and the space of Industrial IoT as previously tackled (with strong growth numbers predicted in ample research) but also can be seen in the number of inventions and thus patent applications, specifically in the – very broad – scope of smart connected objects.
The largest growth of fourth industrial revolution related patent applications is for the sector of enabling technologies, including 3D systems, artificial intelligence and power supply (EPO)
According to the European Patent Office (EPO) in the last three years, the number of European patent applications related to smart connected objects and, thus, to the cyber-physical space of Industrial IoT and related technologies in an Industry 4.0 and manufacturing technologies context has increased by an impressive 54 percent.
However, it’s not about Industrial IoT and smart connected objects themselves alone, nor just about manufacturing or European patent applications.

According to the first landscaping study on “Patents and the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR)”, which was conducted by the European Patent Office in collaboration with German Handelsblatt Research Institute, the impact of the smart object technology trend is happening across a broad range of technical fields.
The study doesn’t only look at Europe (although that’s the key focus) but also looks at patent filings from the US, Japan, China and more, whereby Asia has been stepping up the pace significantly (always in the scope of patents filed with the EPO).
4IR inventions and industrial transformation technologies patent applications: 3 areas and levels
Whether it concerns smart connected objects and IoT, cyber-physical systems and other technologies of Industry 4.0 (or other frameworks across the globe describing the technological and other evolutions in the scope of 4IR): they obviously don’t stand on their own and fit in a context of several related technologies that make them possible, enable them and lead to applications in an increasingly converging context.
As often mentioned before it’s in the combination of technologies and their purpose that digital transformation strategies and Industry 4.0 value (along with processes, people, societal challenges and so on) need to be seen.
In Europe, Germany and France lead in 4IR technology innovation and patent applications, with Germany leading in the sector of application-related technologies and France in the sector of enabling Industry 4.0 technologies (EPO)
And just as the IoT has its IoT stack with various layers of technologies, starting from the ‘things’, sensors, actuators and other embedded technologies (e.g. communication within the scope of the edge where this first layer of connected objects in the IoT stack sits), so isn’t Industry 4.0 just a matter of prioritized steps and the interconnection of several technological and other layers (including the integration of IT and OT) but also of several technologies that are needed to simply enable the optimization and maturity of Industry 4.0 projects and applications in which these smart connected objects find their place.
The press release about the “Patents and the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR)” report distinguished between three levels in this regard, which they call the three relevant technology sectors of the fourth industrial revolution whereby they examined over 48,000 patent applications across each of those Industry 4.0 technology sector.
4IR technology sector 1: the core technology areas
This 4IR sector, which is at the same time a first layer, is the sector comprising the hardware, software and connectivity technologies that simple make smart connected objects and the IoT in an industrial transformation context possible.
They make it possible to build smart connected objects and/or to make objects smart and connected in the sense of IoT and Internet connectivity.
Think about, among others, chips and MEMS, (micro-electromechanical systems), transducers, essential data technologies, core embedded software, memory components, CPUs, intelligence and network/communication capabilities (network protocols), M2M boards and the basic ICT technologies which are needed, among others on the computing, data, operating system and virtualization level.
4IR technology sector 2: the enabling technologies
Having things connected, enabling them to communicate and allowing for essential computing operations is of course not enough.

The layer of enabling technologies (and thus also the sector of these enabling technologies for which the filing of inventions and patent application have been checked) as the name and press release indicate, are the enabling technologies which complement the core technologies.
Simply said: they form the bridge between the smart connected object and the actual application. Think about user interfaces, power supply and artificial intelligence but also about Big Data analytics, the essential systems for support of 3D (and augmented reality, digital twin simulation, additive manufacturing and so on) and systems needed to understand the context of the connected object, which isn’t such a matter of the gathered and communicated data but also, for example, about position of the object and other contextual parameters which are essential for Industry 4.0 applications (acceleration, rotation, movement, the list is long).
Last but not least, also cybersecurity fits here: Industry 4.0 applications aren’t applications if security is not embedded, smart connected objects can’t be used in a smart way without the proper security, plain and simple.
4IR technology sector 3: the actual applications
Here layer 1 and 2 (and thus technology sector 1 and 2) result, within the scope of the 4IR context, in all the technologies which make the applications applicable in real life across all those smart and intelligent domains.
These range from wearables and smart homes to smart buildings, smart cities, smart grids and of course the smart factories of smart manufacturing, still the main application area of Industry 4.0.
Or as the press release puts it: application domains of these technologies, such as vehicles, enterprise and home.
The rise of Industry 4.0 technology patent applications: sectors, regions, patterns and conclusions
Keeping the three mentioned technology sectors, as defined by the European Patent Office, in mind a first finding, as said, is that patent applications in relation with smart objects in the broadest 4IR context are on the rise.
With a growth rate of 54 percent the number of Industry 4.0 technology related patent applications by far outweighs patent applications overall (growth of 7.65 percent). In 2016 alone, for instance, over 5,000 patent applications in the 4IR context filed with the EPO concerned Europe. Do note that data for 2017 are not known yet.
A second finding is that most of the invents which were filed concern the application sector and thus the several new application domains and the core technologies. However, the largest growth is seen in the enabling technology sector, where 3D systems, artificial intelligence and power supply are particularly mentioned.
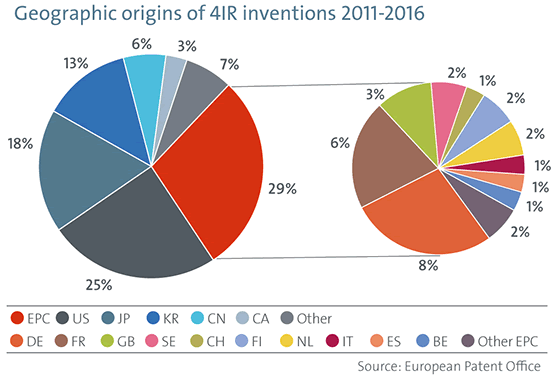
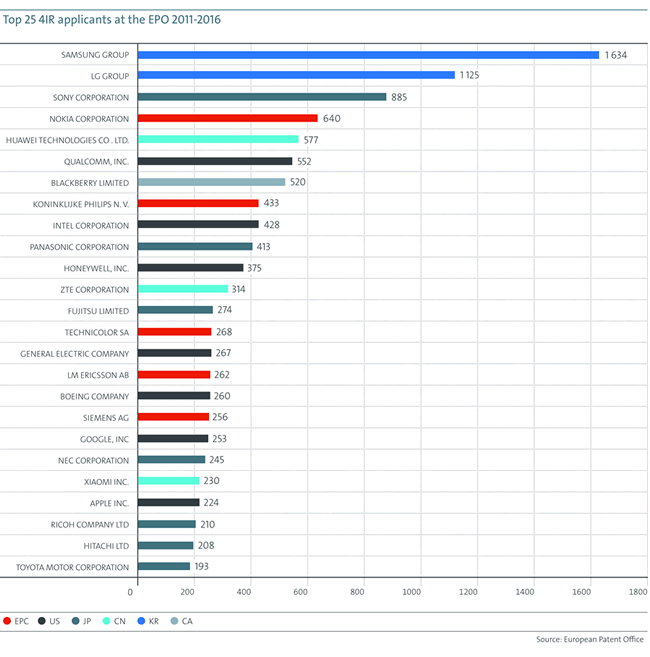
A third finding relates to the regions with most inventions filed in the scope of fourth industrial revolution technologies. According to the press release the main innovation centers from this perspective were Europe, the US and Japan (when looking at patents filed with the EPO). However, the pace of growth of inventions with patent applications filed with the European Patent Office, has been higher from the Republic of Korea and in China with patent applications in the latter two countries coming from a few of the larger ICT companies such as Samsung, Huawei, LG, ZTE and the others you undoubtedly know (the top 25 of companies with fourth industrial revolution technologies patent applications at the EPO is listed below).
Within Europe, Germany and France take the lead whereby Germany stands out in the application-related inventions and sector and France in enabling technologies.
Important: over half of all the filed patent applications come from 25 companies of which most are located in Asia.
A final note: the patent applications confirm the evolution towards ever more convergence on various Industry 4.0 technology levels and the report highlights two case studies around Industry 4.0 technologies (namely additive manufacturing and smart sensors) and two case studies on the application level (being smart manufacturing and smart health).
More in the press release and in the report (PDF opens).
Top image: Shutterstock – Copyright: phive – All other images are the property of their respective mentioned owners.

