Agentic AI ranks high on the list of evolutions in artificial intelligence. Enabling systems to make (semi-)autonomous decisions and take action without direct human input, agentic AI is seen as a key driver of a next phase in AI and digital transformation and is placed at the top of Gartner’s top 10 strategic technology trends for 2025.
The attention for and awareness about artificial intelligence got a big boost in late 2022 with the launch of ChatGPT. The now universally known LLM-based GenAI chatbot was embraced at an unprecedented pace by various user groups for different purposes.
In early 2023, the interest in artificial intelligence visibly increased, as Google Trends clearly shows. Large language models, generative AI, and ChatGPT are only parts and expressions of the field of artificial intelligence.

However, the fascination and use of OpenAI’s ChatGPT and the emergence of more and more GenAI applications, together with a plethora of opinions, media coverage, and a host of new types of outputs (such as images), have led to a growing awareness of artificial intelligence and its possibilities.
The rise of GenAI got so much attention that people who previously were unfamiliar with AI now and then started equating the fascinating world of generative AI with AI in general. These days, you can hardly attend a webinar or other presentation without the speaker pointing out – or reminding – that AI is more than GenAI.
The surge of interest in AI, driven by the rapid adoption of generative AI tools like ChatGPT, has created excitement and misconceptions. While GenAI revolutionizes content generation, businesses are now shifting focus toward AI that generates and acts, leading to the rise of agentic AI, where intelligent agents make decisions and execute tasks autonomously.
“Today’s AI models perform tasks such as generating text, but these are “prompted” — the AI isn’t acting by itself. That is about to change with agentic AI, or AI with agency.” (Tom Coshow, Gartner)
Agentic AI: focus on making decisions with intelligent AI agents that can act
Although much attention is still focused on chatbots and GenAI, the arrival of alternative players and approaches, along with the first disappointments and evolution of AI adoption, is making the focus in the market shift to action-oriented applications and relevant use cases rather than all the underlying techniques and models.
Consequently, for some time now, the focus has been increasingly on agentic AI, where intelligent agents are used to perform specific tasks and autonomously make decisions to achieve user-defined goals, combining AI, automation, and real-time decision-making.
With those intelligent agents, the emphasis is on (semi-)autonomous actions and thus the ability and autonomy to act (“have agency”). LLM-based GenAI applications are more about a generated output (text, code, images, you name it) based on prompts by the user, the AI does not act autonomously.
Intelligent AI agents can perform more complex tasks, and to do so, they use the techniques and tools we typically associate with LLMs and GenAI. However, they can employ more techniques and technologies to achieve their goal. These include just about any form of AI and other technologies and data sources (via APIs), depending on the use case or task they need to accomplish. In short, they can go much further and take action independently or autonomously in the process.
In what direction developments in agentic AI will go isn’t sure yet. Still, some trends and evolutions are becoming apparent, as are the characteristics of use cases where agentic AI is valuable. Gartner points out that AI agency is still low and that proper full-fledged agentic AI systems that can learn from their environment, make decisions, and perform tasks – independently – are for the future.
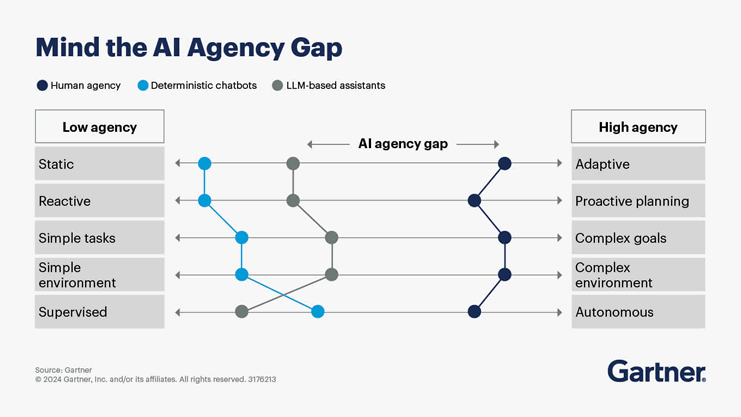
For Gartner, AI agency is a spectrum. You have traditional systems with limited capacity to perform specific tasks under well-defined conditions at one end of that spectrum. They lack autonomy and are typically rule-based. Current GenAI chatbots fall closer to low-agency AI, as they don’t proactively act without user input. It’s also where you find today’s LLM-based assistants. At the other end of the spectrum, there are those future full-fledged agentic AI systems that will continuously learn, make autonomous decisions, and take action without constant human input. And there is still a wide gap between the two ends of the spectrum. How that gap will be closed is for the next few years.
At the same time, things can move fast. In late October 2024, Gartner unveiled the top 10 strategic technology trends organizations should explore and discover in 2025 because they will play a significant role, according to its analysts. Agentic AI was at the very top of the list.
The research and consulting firm defined agentic AI systems as systems that autonomously plan and take actions to achieve user-defined goals when announcing the 10 trends.
Moreover, Gartner predicts that by 2028, at least 15% of daily business decisions will be influenced or made autonomously by agentic AI systems, streamlining workflows and reducing human intervention in routine tasks. That’s an extraordinary amount, considering that in 2024, this was the case for…0% of daily work decisions.
In short, agentic AI is hot. Its position at the peak of Gartner’s AI Hype Cycle reflects the excitement and investments in agentic AI. While many vendors are working on new platforms and applications, businesses must focus on understanding its real potential beyond the hype.
Also check out the AI top trends for 2025 per Gartner.
Top image purchased under license Adobe Stock, all other images belong to their respective mentioned owners and serve illustration purposes.






